Objectives
Materials
Key Questions
-
Part 1:
- Did the balls swing with the same rhythm?
- Which one has the highest natural frequency (sways back and forth the fastest)?
- Have you ever felt a short building sway in the wind? A tall building?
-
Part 2:
- Which wire swung harder?
- Which had the highest natural frequency? The lowest? (The wider "building" will generally have the higher natural frequency due to its stiffness.)
- How does this relate to building structure?
-
Part 3:
- Which ball-and-wire combination has the lowest natural frequency (sways back and forth the slowest)? (The heavier "buildings" will have the lowest natural frequency.)
-
Part 4:
- What did you observe with the big ball? The small ball?
- Which one moved the most? Why?
What To Do
Part 1 (about 20 mins.)
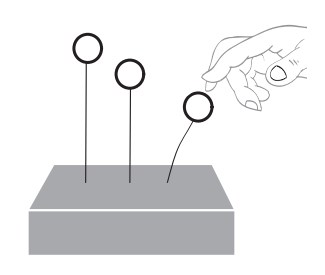
- Roll three pieces of plasticine into balls about 2 cm in diameter.
- Stick a piece of wire (all the same thickness) into the middle of each of the plasticine balls.
- Push the wire (the end away from the plasticine ball) into the block so that the balls are all at different heights; 10, 15 and 20 cm work well. The plasticine represents the weight of the building and the wire represents the flexibility of the building.
- Pull the ball on the tallest wire back about 3 cm, then let go.
- Repeat this for the other plasticine balls.
Part 2 (about 10 mins.)
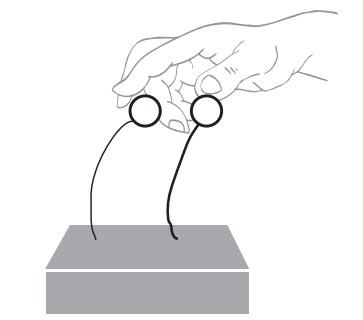
- Roll two pieces of plasticine into balls about 2 cm in diameter.
- Stick a piece of wire into each plasticine ball, as in Part 1, but this time use different thicknesses of wire.
- Push the wire (the end away from the plasticine ball) into the block so that the balls stand at the same height. The plasticine represents the weight of the building and the wire represents the flexibility of the building.
- Pull both balls back about 3 cm, then let go.
Part 3 (about 10 mins.)
- Roll three pieces of plasticine into three different-sized balls. Diameters of 1 cm, 2 cm and 3 cm work well.
- Stick a piece of wire (all the same thickness) into each ball and push the wires into the block so that the balls are at a height of about 15 cm.
- Pull all three balls once and compare what happens.
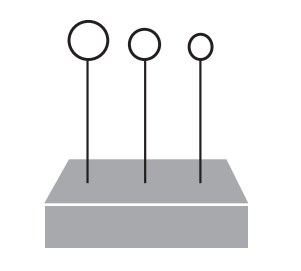
- (Note: If you don’t see a difference, re-roll the balls so that you have a greater variation of size, then re-test.)
Part 4 (about 10 mins.)
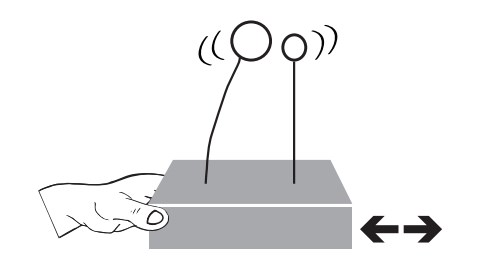
- Roll one small and one bigger plasticine ball.
- Stick them onto two pieces of wire (same thickness) and push them into the block at the same height. About 20 cm would work well.
- Pull the bigger ball back about 3 cm, then let go.
- As the students watch the ball swing, ask them to make a note of the rate and speed at which the ball moves back and forth. This is its natural frequency.
- Now, make an earthquake! Push the block back and forth in time with the ball’s movement. In other words, you’re wiggling the block at the natural frequency of the ball.
- Notice how two motions amplify when they are moving in the same direction at the same time. This is known as resonance.
- Repeat with the smaller ball. What is different?
Extensions
-
What other things can affect the natural frequency of buildings?
-
How would that affect the vulnerability of buildings during an earthquake?
-
Which would be more likely to fall: a building with a higher or lower natural frequency?
Other Resources
IRIS Earthquake Science | How will 3 buildings, engineered equally, on different bedrock, react to an earthquake?
Government of British Columbia | Master of Disaster Youth Education
Government of British Columbia | Earthquake Preparedness and Response
Government of Canada | Natural Resources Canada | Earthquakes Canada
U.S. Geological Survey | Earthquake Hazards Program | Earthquakes for Kids
Cybersleuth Kids | Earthquake Resources






